Bestsellers
-

Zhongdi ZD-129 Magnifying LED Desk Lamp
Deze bureaulamp is ideaal voor op uw werkplek. Met de 5-inch 5D-lens kunnen de subtielste klusjes worden gedaan. De lamp heeft 80 geïntegreerde leds. Kenmerken Lens grootte: 5 inch Lens materiaal: glas Dioptrie: 5D Lichtbron: T5 22 W fluorescentielamp (80 stuks leds) Standaard montage: tafelvoet Spanning: 220-240 V Vermogen: 22 W
€ 50,00
-

Elektor Digital Analogue Video (E-book)
This book is intended for electronics enthusiasts and professionals alike, who want a much deeper understanding of the incredible technology conquests over the pre-digital decades that created video. It details evolution of analogue video electronics and technology from the first electro-mechanical television, through advancements in Cathode Ray Tubes, transistor circuits and signal processing, up to the latest analogue, colour-rich TV, entertainment devices and calibration equipment. Key technological advances that enabled monochrome video and, eventually, colour are explained. The importance, compromises and techniques of maintaining crucial backward legacy compatibilities are described. The generation, signal processing and playback of analogue video signals in numerous capture, display, recording and playback devices together with operating principles and practices are examined. Technical and, often, political merits and deficiencies of key national and international video standards are highlighted. Several formats are shown to win and ultimately to co-exist. This book begins at fairly basic levels; concepts are introduced with human physiological perceptions of light and colour explained. This leads to the subject matter of luminance and chrominance; their equations and the circuits to process. There is full, detailed analysis of waveform shapes and timings inside video equipment and relevant popular connections e.g. S-video. Several analogue video projects which you can build yourself are also included in this book; with schematics, circuit board layouts and calibration steps to help you obtain the best results. The book makes use of many colour pages where the subject matter demands it (e.g. test cards). If you really want a deeper understanding of analogue video then this book is for you!
€ 24,95
Leden € 19,96
-

Elektor Digital H0W2: Get Started with the SensorTile.box (E-book)
STmicroelectronics’ wireless IoT & wearable sensor development kit ‘SensorTile.box’ is a portable multi-sensor circuit board housed in a plastic box and developed by STMicroelectronics. It is equipped with a high-performance 32-bit ARM Cortex-M4 processor with DSP and FPU, and various sensor modules, such as accelerometer, gyroscope, temperature sensor, humidity sensor, atmospheric pressure sensor, microphone, and so on. SensorTile.box is ready to use with wireless IoT and Bluetooth connectivity that can easily be used with an iOS or Android compatible smartphone, regardless of the level of expertise of the users. SensorTile.box is shipped with a long-life battery and all the user has to do is connect the battery to the circuit to start using the box. The SensorTile.box can be operated in three modes: Basic mode, Expert mode, and Pro mode. Basic mode is the easiest way of using the box since it is pre-loaded with demo apps and all the user has to do is choose the required apps and display or plot the measured data on a smartphone using an app called STE BLE Sensor. In Expert mode users can develop simple apps using a graphical wizard provided with the STE BLE Sensor. Pro mode is the most complex mode allowing users to develop programs and upload them to the SensorTile.box. This book is an introduction to the SensorTile.box and includes the following: Brief specifications of the SensorTile.box; description of how to install the STE BLE Sensor app on an iOS or Android compatible smartphone required to communicate with the box. Operation of the SensorTile.box in Basic mode is described in detail by going through all of the pre-loaded demo apps, explaining how to run these apps through a smartphone. An introduction to the Expert mode with many example apps developed and explained in detail enabling users to develop their own apps in this mode. Again, the STE BLE Sensor app is used on the smartphone to communicate with the SensorTile.box and to run the developed apps. The book then describes in detail how to upload the sensor data to the cloud. This is an important topic since it allows the sensor measurements to be accessed from anywhere with an Internet connection, at any time. Finally, Pro mode is described in detail where more experienced people can use the SensorTile.box to develop, debug, and test their own apps using the STM32 open development environment (STM32 ODE). The Chapter explains how to upload the developed firmware to the SensorTile.box using several methods. Additionally, the installation and use of the Unicleo-GUI package is described with reference to the SensorTile.box. This PC software package enables all of the SensorTile.box sensor measurements to be displayed or plotted in real time on the PC.
€ 29,95
Leden € 23,96
-

NXP Semiconductors NXP FRDM-MCXN947 Development Board
The FRDM-MCXN947 is a compact and versatile development board designed for rapid prototyping with MCX N94 and N54 microcontrollers. It features industry-standard headers for easy access to the MCU's I/Os, integrated open-standard serial interfaces, external flash memory, and an onboard MCU-Link debugger. Specificaties Microcontroller MCX-N947 Dual Arm Cortex-M33 cores @ 150 MHz each with optimized performance efficiency, up to 2 MB dual-bank flash with optional full ECC RAM, External flash Accelerators: Neural Processing Unit, PowerQuad, Smart DMA, etc. Memory Expansion *DNP Micro SD card socket Connectivity Ethernet Phy and connector HS USB-C connectors SPI/I²C/UART connector (PMOD/mikroBUS, DNP) WiFi connector (PMOD/mikroBUS, DNP) CAN-FD transceiver Debug On-board MCU-Link debugger with CMSIS-DAP JTAG/SWD connector Sensor P3T1755 I³C/I²C Temp Sensor, Touch Pad Expansion Options Arduino Header (with FRDM expansion rows) FRDM Header FlexIO/LCD Header SmartDMA/Camera Header Pmod *DNP mikroBUS User Interface RGB user LED, plus Reset, ISP, Wakeup buttons Inbegrepen 1x FRDM-MCXN947 Development Board 1x USB-C Cable 1x Quick Start Guide Downloads Datasheet Block diagram
€ 29,95€ 11,98
Leden identiek
-
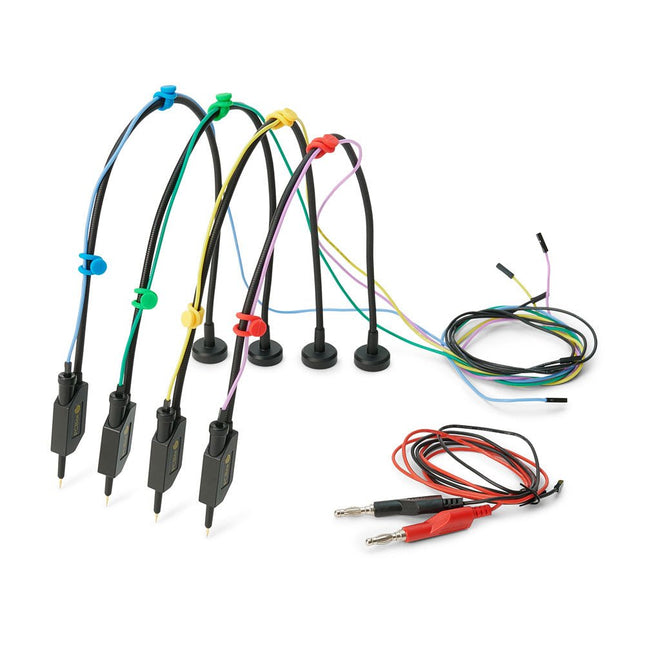

Sensepeek Sensepeek 6005 4x SQ10 Probe incl. Test Wires
The SQ series of handsfree PCBite probes from Sensepeek are insulated, come with included color-coded cable holders and have a lower point of gravity making them even more stable compared with the original SP series of probes. All the loved features of handsfree measurement, exchangeable fine pitch spring tipped test needle and the minimalistic design is maintained to make traditional sized and handheld probes obsolete. Features All handsfree probes from Sensepeek makes instant measurements or long triggering sessions a breeze. No more soldering wires to connect your probe or complicated tools to setup, just positioning the probe needle on any test point or component in the signal path and release. Saves time and frustration during development, verification and repairs. The minimalist design and the spring-loaded test needle makes it possible to simultaneously measure on fine pitch components and nearby signals. Both length and weight of the SQ probes are perfectly balanced to be used with PCBite PCB holders and base plate which is a must for handsfree function. The probe holder comes with a powerful magnet in the base, as for all PCBite probes and holders which makes the probe easy to place and reposition. The SQ series of probes can be used handheld without the probe holder as they have an insulated grip but their full potential is used when measuring handsfree. Included 4x SQ10 probes and pin tipped test needles (black) 2x Banana to dupont test wires (red/black) 5x Dupont to dupont test wires 1x Set of cable holders (4 colors) 4x Extra test needles Downloads User guide
€ 107,69
-

Elektor Digital Elektor Select: Arduino Compilatie (PDF)
Dit 216 pagina's tellende e-book staat boordevol Arduino-ideeën, uitleg, tips, diagrammen, programma's, PCB layouts en meer. Genoeg voor dagen vol informatief, inspirerend en stimulerend leesplezier! Opgemaakt als PDF bevat dit digitale document een inhoudsopgave inclusief links naar elk project, zo dat u gemakkelijk komt waar u wilt zijn. Dit biedt u de mogelijkheid om tussen projecten te wisselen en degene die u het meeste boeien snel en gemakkelijk te vinden.
€ 9,95
Leden € 7,96
-

Elektor Digital RFID (E-book)
RFID technology has conquered many areas in which barcodes, magnetic strips and contact smartcards were used previously. Everyday applications, such as electronic ticketing, access cards, debit cards and electronic identity documents would not be possible without this technology. MIFARE is the most widely used RFID technology, and this book provides a practical and comprehensive introduction to it. Among other things, the initial chapters cover physical fundamentals, relevant standards, RFID antenna design, security considerations and cryptography. The complete design of a reader’s hardware and software is described in detail. The reader’s firmware and the associated PC software support programming using any .NET language. The specially developed PC program, “Smart Card Magic.NET”, is a simple development environment that supports sending commands to a card at the click of a mouse, as well as the ability to create C# scripts. Alternatively, one may follow all of the examples using Visual Studio 2010 Express Edition. Finally, the major smart card reader API standards are introduced. The focus is on programming contactless smartcards using standard PC/SC readers using C/C++, Java and C#.
€ 34,95
Leden € 27,96
-
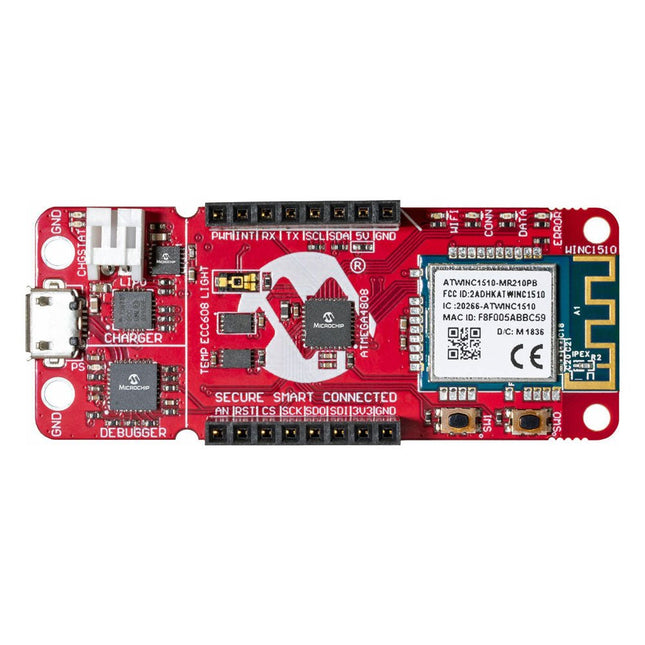
Microchip Microchip AVR-IoT WA Development Board
The AVR-IoT WA development board combines a powerful ATmega4808 AVR MCU, an ATECC608A CryptoAuthentication™ secure element IC and the fully certified ATWINC1510 Wi-Fi network controller – which provides the most simple and effective way to connect your embedded application to Amazon Web Services (AWS). The board also includes an on-board debugger, and requires no external hardware to program and debug the MCU.Out of the box, the MCU comes preloaded with a firmware image that enables you to quickly connect and send data to the AWS platform using the on-board temperature and light sensors. Once you are ready to build your own custom design, you can easily generate code using the free software libraries in Atmel START or MPLAB Code Configurator (MCC).The AVR-IoT WA board is supported by two award-winning Integrated Development Environments (IDEs) – Atmel Studio and Microchip MPLAB X IDE – giving you the freedom to innovate with your environment of choice.Features ATmega4808 microcontroller Four user LED’s Two mechanical buttons mikroBUS header footprint TEMT6000 Light sensor MCP9808 Temperature sensor ATECC608A CryptoAuthentication™ device WINC1510 WiFi Module On-board Debugger Auto-ID for board identification in Atmel Studio and Microchip MPLAB X One green board power and status LED Programming and debugging Virtual COM port (CDC) Two DGI GPIO lines USB and battery powered Integrated Li-Ion/LiPo battery charger
€ 39,95€ 15,98
Leden identiek
-

SDRplay SDRplay RSP1B 14-bit SDR-ontvanger (1 kHz tot 2 GHz)
De SDRplay RSP1B is een verbeterde versie van de populaire RSP1A – een krachtige, breedbandige, complete 14-bits SDR die het RF-spectrum van 1 kHz tot 2 GHz bestrijkt. De RSP1B is uitgevoerd in een robuuste, zwartgelakte stalen behuizing en biedt aanzienlijk verbeterde ruisprestaties. Het enige wat nodig is, is een computer en een antenne voor uitstekende communicatie- en ontvangstfunctionaliteit. Het wordt geleverd met SDRuno voor Windows en de multi-platform SDRconnect-software voor Windows, macOS en Linux (gratis geleverd door SDRplay). U kunt tot 10 MHz spectrum tegelijk monitoren. Een gedocumenteerde API stelt ontwikkelaars in staat om nieuwe demodulatoren of applicaties voor het platform te creëren. Kenmerken Covers all frequencies from 1 kHz through VLF, LF, MW, HF, VHF, UHF and L-band to 2 GHz, with no gaps Receive, monitor and record up to 10 MHz of spectrum at a time Free use of windows-based SDRuno software which provides an ever-increasing feature-set Strong and growing software support network Calibrated S meter/ RF power and SNR measurement with SDRuno (including datalogging to .CSV file capability) Documented API provided to allow demodulator or application development on multiple platforms Excellent dynamic range for challenging reception conditions Works with popular 3rd party SDR software (including HDSDR, SDR Console and Cubic SDR) ExtIO based plugin available Software upgradeable for future standards Strong and growing software support network API provided to allow demodulator or application development Multiplatform driver and API support including Windows, Linux, Mac, Android and Raspberry Pi Up to 16 individual receivers in any 10 MHz slice of spectrum using SDRuno Calibrated S meter and power measurements with SDRuno Stand-alone windows-based spectrum analyser software available (with sweep, sample and hold features) Ideal for monitoring of ISM/IoT/Telemetry bands <2 GHz Ideal for portable operation Specificaties Frequency Range 1 kHz – 2 GHz Antenna Connector SMA Antenna Impedance 50 Ohms Current Consumption (Typical) 185 mA (excl. Bias-T) USB Connector USB Type B Maximum Input Power +0 dBm Continuous+10 dBm Short Duration ADC Sample Rates 2-10.66 MSPS ADC Number of Bits 14 bit 2-6.048 MSPS12 bit 6.048-8.064 MSPS10 bit 8.064-9.216 MSPS8 bit >9.216 MSPS Bias-T 4.7 V100 mA guaranteed Reference 0.5ppm 24 MHz TCXO.Frequency error trimmable to 0.01ppm in field. Operating Temperature Range -10✓C to +60✓C Dimensions 98 x 88 x 34 mm Weight 110 g Downloads Datasheet Software RSP1B vs RSPdx vs RSPduo RSP1B RSPdx RSPduo Continuous coverage from 1 kHz to 2 GHz ✓ ✓ ✓ Up to 10 Mhz visible bandwidth ✓ ✓ ✓ 14-bit ADC silicon technology plus multiple high-performance input filters ✓ ✓ ✓ Software selectable AM/FM & DAB broadcast band notch filters ✓ ✓ ✓ 4.7 V Bias-T for powering external remote antenna amplifier ✓ ✓ ✓ Powers over the USB cable with a simple type B socket ✓ ✓ ✓ 50✓ SMA antenna input(s) for 1 kHz to 2 GHz operation (software selectable) 1 2 2 Additional software selectable Hi-Z input for up to 30 Mhz operation ✓ Additional software selectable 50✓ BNC input for up to 200 MHz operation ✓ Additional LF/VLF filter for below 500 kHz ✓ 24 MHz reference clock input (+ output on RSPduo) ✓ ✓ Dual tuners enabling reception on 2 totally independent 2 MHz ranges ✓ Dual tuners enabling diversity reception using SDRuno ✓ Robust and strong plastic case (with internal RF shielding layer) ✓ Rugged black painted steel case ✓ ✓ Overall performance below 2 MHz for MW and LF + ++ + Multiple simultaneous applications + + ++ Performance in challenging fading conditions (*using diversity tuning) + + *++
€ 148,99
-
Elektor Academy Pro Design PCBs Like a Pro
Leer KiCad met Peter Dalmaris De Academy Pro Box "Design PCBs like a Pro" biedt een compleet, gestructureerd trainingsprogramma in PCB-ontwerp, dat online leren combineert met praktische toepassing. Gebaseerd op de KiCad-cursus van Peter Dalmaris, integreert het 15 weken durende programma videolessen, gedrukt materiaal (2 boeken) en praktijkgerichte projecten om ervoor te zorgen dat deelnemers niet alleen de theorie begrijpen, maar ook de vaardigheden ontwikkelen om deze in de praktijk toe te passen. In tegenstelling tot standaardcursussen biedt de Academy Pro Box een begeleid leertraject met wekelijkse mijlpalen en fysieke componenten om werkende PCB's te ontwerpen, testen en produceren. Deze aanpak ondersteunt een diepgaandere leerervaring en een betere kennisbehoud. De box is ideaal voor ingenieurs, studenten en professionals die praktische expertise in PCB-ontwerp willen ontwikkelen met behulp van open-sourcetools. Met de extra optie om hun afstudeerproject te laten produceren, ronden deelnemers het programma af met echte resultaten – klaar voor gebruik, testen of verdere ontwikkeling. Learn by doing Vaardigheden ontwikkelen. Echte printplaten ontwerpen. Gerbers genereren. Je eerste bestelling plaatsen. Dit is niet zomaar een cursus – het is een compleet projecttraject van idee tot product. Wat u leert/ontvangt Werkkennis van de tools van KiCad Vertrouwen in het ontwerpen van uw eigen printplaten (PCB’s) Een volledig produceerbare printplaat – door u zelf gemaakt Wat zit er in de doos (cursus)? Beide delen van "KiCad Like a Pro" (t.w.v. € 105) Vol 1: Fundamentals and Projects Vol 2: Advanced Projects and Recipes Couponcode voor deelname aan de bestseller KiCad 9 online cursus van Peter Dalmaris op Udemy, met meer dan 20 uur aan videotraining. U voltooit drie volledige ontwerpprojecten: Breadboard voeding Kleine zonne-energie voeding Datalogger met EEPROM en klok Voucher van Eurocircuits voor de productie van printplaten (t.w.v. € 85 excl. BTW) Leermateriaal (van deze box/cursus) 15-weken leerprogramma ▶ Klik hier om te openen Week 1: Setup, Fundamentals, and First Steps in PCB Design Week 2: Starting Your First PCB Project – Schematic Capture Week 3: PCB Layout – From Netlist to Board Design Week 4: Design Principles, Libraries, and Workflow Week 5: Your First Real-World PCB Project Week 6: Custom Libraries – Symbols, Footprints, and Workflow Week 7: Advanced Tools – Net Classes, Rules, Zones, Routing Week 8: Manufacturing Files, BOMs, and PCB Ordering Week 9: Advanced Finishing Techniques – Graphics, Refinement, and Production Quality Week 10: Tiny Solar Power Supply – From Schematic to Layout Week 11: Tiny Solar Power Supply – PCB Layout and Production Prep Week 12: ESP32 Clone Project – Schematic Design and Layout Prep Week 13: ESP32 Clone – PCB Layout and Manufacturing Prep Week 14: Final Improvements and Advanced Features Week 15: Productivity Tools, Simulation, and Automation KiCad-cursus met 18 lessen op Udemy (door Peter Dalmaris) ▶ Klik hier om te openen Introduction Getting started with PCB design Getting started with KiCad Project: A hands-on tour of KiCad (Schematic Design) Project: A hands-on tour of KiCad (Layout) Design principles and PCB terms Design workflow and considerations Fundamental KiCad how-to: Symbols and Eeschema Fundamental KiCad how-to: Footprints and Pcbnew Project: Design a simple breadboard power supply PCB Project: Tiny Solar Power Supply Project: MCU datalogger with build-in 512K EEPROM and clock Recipes KiCad 9 new features and improvements Legacy (from previous versions of KiCad) KiCad 7 update (Legacy) (Legacy) Gettings started with KiCad Bonus lecture Over de auteur Dr. Peter Dalmaris, PhD, is docent, elektrotechnisch ingenieur en maker. Hij is maker van online videocursussen over doe-het-zelf-elektronica en auteur van diverse technische boeken. Sinds 2013 is Peter Chief Tech Explorer bij Tech Explorations, het bedrijf dat hij oprichtte in Sydney (Australië). Zijn missie is om technologie te verkennen en de wereld te helpen opleiden. Wat is Elektor Academy Pro? Elektor Academy Pro biedt gespecialiseerde leeroplossingen voor professionals, engineeringteams en technische experts in de elektronica- en embedded systemenindustrie. Het stelt zowel individuen als organisaties in staat hun praktijkkennis te verdiepen, vaardigheden te versterken en voorop te blijven lopen met hoogwaardige content en praktische trainingstools. Van praktijkgerichte projecten en cursussen onder leiding van experts tot diepgaande technische inzichten – Elektor ondersteunt ingenieurs bij het aanpakken van de actuele uitdagingen binnen elektronica en embedded systemen. Ons educatieve aanbod bestaat uit Academy-boeken, Pro Boxes, webinars, conferenties en branchespecifieke B2B-magazines – allemaal ontwikkeld met het oog op professionele groei. Of u nu ingenieur, R&D-specialist of technisch beslisser bent: Elektor Academy Pro slaat de brug tussen theorie en praktijk, helpt u nieuwe technologieën te beheersen en stimuleert innovatie binnen uw organisatie.
€ 199,95€ 164,95
Leden identiek
-

Elektor Digital Retronics (E-book)
Quite unintentionally a one-page story on an old Heathkit tube tester in the December 2004 edition of Elektor magazine spawned dozens of ‘Retronics’ tales appearing with a monthly cadence, and attracting a steady flow of reader feedback and contributions to the series. Since launching his Retronics columns, Elektor Editor Jan Buiting has never been short of copy to print, or vintage equipment to marvel at. This book is a compilation of about 80 Retronics installments published between 2004 and 2012. The stories cover vintage test equipment, prehistoric computers, long forgotten components, and Elektor blockbuster projects, all aiming to make engineers smile, sit up, object, drool, or experience a whiff of nostalgia. To reflect that our memories are constantly playing tricks on us, and honoring that “one man’s rubbish is another man’s gem”, the tales in the book purposely have no chronological order, and no bias in favor of transistor or tube, microprocessor or discrete part, audio or RF, DIY or professional, dry or narrative style. Although vastly diff erent in subject matter, all tales in the book are told with personal gusto because Retronics is about sentiment in electronics engineering, construction and repair, be it to reminisce about a 1960s Tektronix scope with a cleaning lady as a feature, or a 1928 PanSanitor box for dubious medical use. Owners of this book are advised to not exceed one Retronics tale per working day, preferably consumed in the evening hours under lamp light, in a comfortable chair, with a piece of vintage electronic equipment close and powered up.
€ 24,95
Leden € 19,96
-

Elektor Digital ESP32 & ESP8266 Compilatie (E-book)
De ESP8266 van Espressif is een Wi-Fi microchip met volledige TCP/IP stack en functionaliteit van een microcontroller. Het heeft indruk gemaakt in de maker community met zijn lage prijs. Maar veel ontwikkelaars waren ontevreden over het hoge stroomverbruik van de ESP8266. De ESP32, uitgerust met een ULP (Ultra Low Power) coprocessor, biedt hiervoor een oplossing. Dit e-book bevat een aantal projecten met ESP32 & ESP8266 en een interview met de CEO Teo Swee Ann van Espressif. Artikelen Lichtkrant met ESP-12F, 512 LED’s via WiFi aansturen VFD-klok met ESP32, met nauwkeurige internettijd Zuinige ESP32, de programmering van de ULP-coprocessor DCF77-emulator met ESP8266, internettijd vervangt draadloze tijd WiFi desktop-thermostaat, flexibele en programmeerbare temperatuurregeling Timers voor de WiFi desktop-thermostaat, zeven kanalen met atoomprecisie Zwitsers zakmes voor microcontrollers, PlatformIO als universeel programmeertool ESP8266 USB-programmeer-adapter voor de Espressif-modules ESP-01 en ESP-012 De ESP8266 op het Android I/O-board, zelf nieuwe firmware flashen Weerdisplay, actuele weersinformatie op een kleuren-LCD GoNotify, een flexibele IoT sensor-interface. Join the bubble! CV-monitor met ESP8266, domotica voor de overgang naar duurzame energie MicroPython en het pyboard, van een knipperende LED naar … een knipperende LED aan een webserver De grote broer van de ESP8266, de eerste stappen met de ESP32 en de Arduino-IDE RGBDigit klok, een kleurrijk 7-segment-display voor uw data WLAN voor microcontrollers, besturen met de ESP8266 De terugkeer van de Wi-Fi-besturingskaart, apparatuur bedienen met uw smartphone Compact en autonoom WLAN, handig gebruik van de ESP8266 zonder MCU
€ 9,95
Leden € 7,96
-

Elektor Digital Getting Started With Java Using Eclipse (E-book)
Mastering the Language and the Development Platform Many people would like to learn Java but getting started is not easy since programming with Java requires at least two things: mastering the programming language and the development environment. With the help of many examples, this book shows how the language is structured. In addition, it employs the Eclipse development environment as an example of a powerful tool to teach developing Java programs. In Basics, the first part of the book, you acquire your Java and Eclipse basic knowledge. This part lays the programming foundations, gives you an overview of Java technology, and shows you what is special about object-oriented programming. In the second part called Java Language, everything revolves around the subtleties of the Java language and this is where the first small Java applications are created, aided by a fine blend of the knowledge part and practical exercises. Java Technology is both the name and the focus of the third part which also introduces you to the rules to observe when programming, what class libraries are and what advantages they have. In addition, you will learn how to test programs, what algorithms are, and how to program them. The fourth part, Java Projects, enables you to apply all the previous elements in an application with a graphical user interface. The project shows how to develop a larger application piece by piece with the Eclipse development environment. The Appendix concludes with a section on frequent errors that can occur when working with Eclipse, and a Glossary.
€ 34,95
Leden € 27,96
-
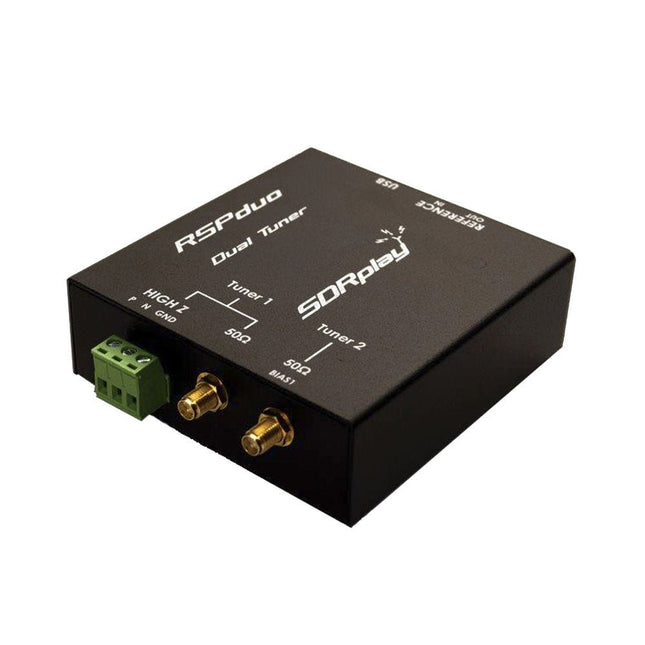

SDRplay SDRplay RSPduo Dual-Tuner 14-bit SDR-ontvanger (1 kHz tot 2 GHz)
De SDRplay RSPduo is een hoogwaardige 14-bit SDR-ontvanger met dubbele tuner. De tuner is ondergebracht in een hoogwaardige stalen behuizing en kan afzonderlijk werken tussen 1 kHz en 2 GHz met een bandbreedte tot 10 MHz. Beide tuners kunnen tegelijkertijd werken tussen 1 kHz en 2 GHz met een bandbreedte tot 2 MHz per tuner. Een zeer stabiele referentie en externe klokfuncties maken dit apparaat ideaal voor industriële, wetenschappelijke en educatieve toepassingen. Kenmerken Dubbele tuner biedt onafhankelijke dekking van 1 kHz tot 2 GHz met behulp van 2 antennepoorten tegelijk 14-bits ADC-siliciumtechnologie Tot 10 MHz zichtbare bandbreedte (enkele tunermodus) of 2 slices van 2 MHz spectrum (dubbele tunermodus) 3 softwarematig selecteerbare antennepoorten (2x 50Ω en 1x 1kΩ hoge impedantie gebalanceerde/ongebalanceerde ingang) Antennepoort met hoge impedantie (1 kHz tot 30 MHz) met selecteerbaar MW-notchfilter en keuze uit 2 voorselectiefilters Softwarematig selecteerbare AM/FM- en DAB-uitzendband-notchfilters voor de 2 SMA-antennepoorten (1 kHz tot 2 GHz) Externe klokinvoer en -uitvoer maken eenvoudige synchronisatie met meerdere RSP's of een externe referentieklok mogelijk Wordt gevoed via de USB-kabel met een eenvoudige type B-aansluiting 11 hoogselectieve, ingebouwde front-end preselectiefilters op beide 2 SMA-antennepoorten Softwarematig selecteerbare multi-level Low Noise voorversterker Bias-T voeding voor het voeden van een op de antenne gemonteerde LNA In een robuuste, zwart gelakte stalen behuizing. SDRuno – SDR-software van wereldklasse voor Windows Gedocumenteerde API voor de ontwikkeling van nieuwe apps Specificaties Frequentiebereik 1 kHz – 2 GHz Antenne-aansluiting SMA Antenne-impedantie 50 ohm Stroomverbruik (typisch) Enkele tunermodus: 180 mA (excl. Bias-T)Dubbele tunermodus: 280 mA (excl. Bias-T) USB-aansluiting USB type B Maximaal ingangsvermogen +0 dBm Continu+10 dBm korte duur ADC-samplefrequenties 2-10,66 MSPS ADC-aantal bits 14 bit 2-6,048 MSPS12 bit 6,048-8,064 MSPS10 bit 8,064-9,216 MSPS8 bit >9,216 MSPS Bias-T 4,7 V100 mA gegarandeerd Referentie Hoge temperatuurstabiliteit (0,5 ppm) 24 MHz TCXOFrequentiefout instelbaar tot 0,01 ppm in het veld Bedrijfstemperatuurbereik −10°C tot +60°C Afmetingen 98 x 94 x 33 mm Gewicht 315 g Downloads Datasheet Detailed Technical Information Software RSPdx-R2 vs RSPduo RSPdx-R2 RSPduo Continue dekking van 1 kHz tot 2 GHz ✓ ✓ Tot 10 MHz zichtbare bandbreedte ✓ ✓ 14-bits ADC siliciumtechnologie plus meerdere krachtige ingangsfilters ✓ ✓ Softwarematig selecteerbare AM/FM & DAB broadcast band notch filters ✓ ✓ 4,7 V Bias-T voor voeding van externe antenneversterker ✓ ✓ Voedt de USB-kabel met een eenvoudige aansluiting type B ✓ ✓ 50Ω SMA-antenne-ingang(en) voor werking van 1 kHz tot 2 GHz (softwarematig instelbaar) 2 2 Extra softwarematig selecteerbare Hi-Z ingang voor werking tot 30 MHz ✓ Extra softwarematig selecteerbare 50Ω BNC-ingang voor werking tot 200 MHz ✓ Extra LF/VLF-filter voor onder 500 kHz ✓ 24 MHz referentieklokingang (+ uitgang op RSPduo) ✓ ✓ Dubbele tuners voor ontvangst op 2 totaal onafhankelijke 2 MHz-bereiken ✓ Dubbele tuners voor diversiteitsontvangst met SDRuno ✓ Robuuste zwartgelakte stalen behuizing ✓ ✓ Algemene prestaties onder 2 MHz voor MW en LF ++ + Meerdere gelijktijdige toepassingen + ++ Prestaties in uitdagende fading-omstandigheden (*met gebruik van diversiteitsafstemming) + *++
€ 287,98
-

Elektor Publishing H0W2: Get Started with the SensorTile.box
STmicroelectronics’ wireless IoT & wearable sensor development kit ‘SensorTile.box’ is a portable multi-sensor circuit board housed in a plastic box and developed by STMicroelectronics. It is equipped with a high-performance 32-bit ARM Cortex-M4 processor with DSP and FPU, and various sensor modules, such as accelerometer, gyroscope, temperature sensor, humidity sensor, atmospheric pressure sensor, microphone, and so on. SensorTile.box is ready to use with wireless IoT and Bluetooth connectivity that can easily be used with an iOS or Android compatible smartphone, regardless of the level of expertise of the users. SensorTile.box is shipped with a long-life battery and all the user has to do is connect the battery to the circuit to start using the box. The SensorTile.box can be operated in three modes: Basic mode, Expert mode, and Pro mode. Basic mode is the easiest way of using the box since it is pre-loaded with demo apps and all the user has to do is choose the required apps and display or plot the measured data on a smartphone using an app called STE BLE Sensor. In Expert mode users can develop simple apps using a graphical wizard provided with the STE BLE Sensor. Pro mode is the most complex mode allowing users to develop programs and upload them to the SensorTile.box. This book is an introduction to the SensorTile.box and includes the following: Brief specifications of the SensorTile.box; description of how to install the STE BLE Sensor app on an iOS or Android compatible smartphone required to communicate with the box. Operation of the SensorTile.box in Basic mode is described in detail by going through all of the pre-loaded demo apps, explaining how to run these apps through a smartphone. An introduction to the Expert mode with many example apps developed and explained in detail enabling users to develop their own apps in this mode. Again, the STE BLE Sensor app is used on the smartphone to communicate with the SensorTile.box and to run the developed apps. The book then describes in detail how to upload the sensor data to the cloud. This is an important topic since it allows the sensor measurements to be accessed from anywhere with an Internet connection, at any time. Finally, Pro mode is described in detail where more experienced people can use the SensorTile.box to develop, debug, and test their own apps using the STM32 open development environment (STM32 ODE). The Chapter explains how to upload the developed firmware to the SensorTile.box using several methods. Additionally, the installation and use of the Unicleo-GUI package is described with reference to the SensorTile.box. This PC software package enables all of the SensorTile.box sensor measurements to be displayed or plotted in real time on the PC.
€ 34,95
Leden € 31,46
-
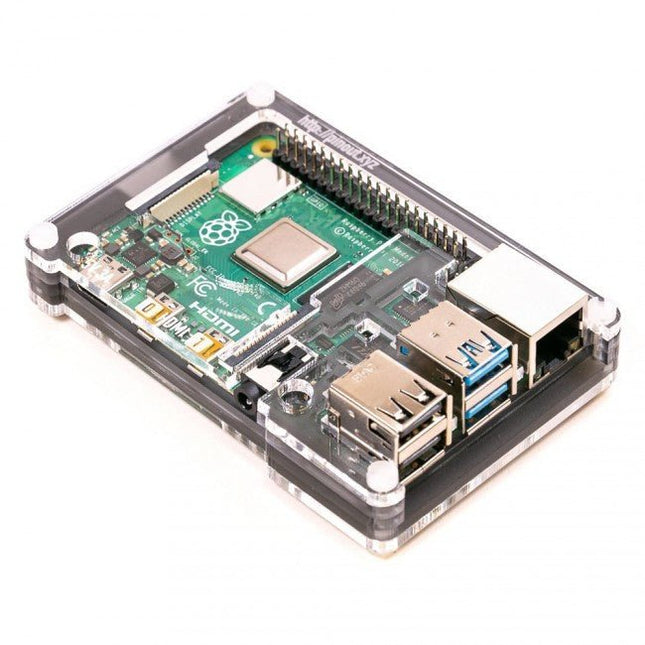

Pimoroni Pibow Coupé 4 (Ninja) - Slim Case for Raspberry Pi 4
Features Compatible with Raspberry Pi 4 only Cutout in lid for 40x30mm heatsink or Fan SHIM Super-slimline profile Fully HAT-compatible Protects your beloved Pi Clear top and base leave Raspberry Pi 4 visible GPIO cut-out Handy laser-etched port labels Leaves all ports accessible Made from lightweight, high-quality, cast acrylic Great for hacking and tinkering! Made in Sheffield, UK Weighing just over 50 grams, the case is lightweight and ideal for mounting to any surface. No tools are required for assembly or disassembly. The dimensions are: 99 × 66 × 15 mm. In the video below you can see a quick assembly guide.
€ 11,95€ 4,78
Leden identiek
-

Elektor Digital Meettechniek in de praktijk (E-book)
Meten is voor een praktiserend elektronicus even vanzelfsprekend als ademhalen. Of het nu om het ontwikkelen van nieuwe schakelingen gaat, de controle van elektronische apparaten tijdens de productiefase of om het foutzoeken in defecte apparatuur: meetapparaten zijn het belangrijkste gereedschap en worden voortdurend gebruikt. 'Weet wat je meet', luidt een bekende uitspraak. En zo is het maar net: om zichzelf geen rad voor ogen te draaien moet de elektronicus weten wat hij doet, moet hij de nauwkeurigheid van zijn meetapparatuur en vooral de voor- en nadelen van de toegepaste meetmethode kennen. En hier steekt dit boek de lezer de helpende hand toe: uitgaand van theoretische beschouwingen en definities van de belangrijkste begrippen van de meettechniek begeleidt het de lezer bij de reis van eenvoudige wijzerinstrumenten via multimeter en oscilloscoop tot en met FFT-analyzers en gespecialiseerde meetapparaten zoals audio-analyzers, geluidsdrukmeters, apparaat- en installatietesters.
€ 29,95
Leden € 23,96
-

Elektor Digital Microcontroller Basics with PIC (E-book)
In this book the author presents all essential aspects of microcontroller programming, without overloading the reader with unnecessary or quasi-relevant bits of information. Having read the book, you should be able to understand as well as program, 8-bit microcontrollers. The introduction to microcontroller programming is worked out using microcontrollers from the PIC series. Not exactly state-of-the-art with just 8 bits, the PIC micro has the advantage of being easy to comprehend. It is offered in a DIP enclosure, widely available and not overly complex. The entire datasheet of the PIC micro is shorter by decades than the description of the architecture outlining the processor section of an advanced microcontroller. Simplicity has its advantages here. Having mastered the fundamental operation of a microcontroller, you can easily enter into the realms of advanced softcores later. Having placed assembly code as the executive programming language in the foreground in the first part of the book, the author reaches a deeper level with ‘C’ in the second part. Cheerfully alongside the official subject matter, the book presents tips & tricks, interesting measurement technology, practical aspects of microcontroller programming, as well as hands-on options for easier working, debugging and faultfinding.
€ 32,95
Leden € 26,36
-

Elektor Digital Initiation au langage CircuitPython et à la puce nRF52840 (E-book)
Le langage de programmation Python est apprécié par les pédagogues parce que sa syntaxe le rend facile à comprendre. Il s'est également imposé chez les informaticiens expérimentés. La société Adafruit a développé une version spéciale de Python pour l'embarquer sur les microcontrôleurs à 32 bits : CircuitPython. Ce livre permettra au lecteur de s'initier à la programmation en CircuitPython sur deux cartes : Feather BlueFruit Sense (également appelée Feather nRF52840 Sense) et CLUE nRF52840 Express. Chacune est animée par le SoC nRF52840 de NORDIC avec une architecture à 32 bits. Pour ce voyage dans le monde de la programmation embarquée, l'auteur sort du chemin classique, à savoir un cours complet sur la programmation orientée objet appliquée à ce langage. Il préfère emmener le lecteur directement sur le terrain avec des projets qui mettent en oeuvre les cartes et différents périphériques. Plus d'une quarantaine d'exemples et de montages permettent de découvrir la richesse de CircuitPython. Toutefois l'auteur s'est imposé une limite pour ne pas décourager les novices : le code de chaque projet ne dépasse jamais la centaine de lignes. Pour ce qui est du matériel, là aussi la simplicité domine : aucun programmateur, un simple PC suffit ; aucun soudage grâce au câblage sur platine d'essai. Les cartes d'extension FeatherWing à enficher sur la Feather nRF52840 Sense permettent de démultiplier ses fonctions : matrice de LED, enregistreur de données, écran à encre électronique, écran OLED, écran TFT, commande de moteurs, audio, relais… Toutes les étapes (assemblage des différents composants, installation des bibliothèques requises, programmation, tests…) sont expliquées en détail. Le code des différents exemples et projets est disponible sur Github. Le résultat de chaque projet est même présenté sur de courtes vidéos disponibles sur YouTube. À la fin de sa lecture, le nouveau Pythonien pourra facilement approfondir les notions abordées et donner vie à ses propres projets grâce aux outils qu'il aura essayés. Ce livre s'adresse aux lycéens et étudiants ainsi qu'à toute la communauté des makers. Chaîne YouTube de l'auteur YouTube (Michaël Bottin)
€ 34,95
Leden € 27,96
-

OWON OWON OW18B Bluetooth Multimeter
Features Data-logger & Multimeter & Thermometer 3 (5/6) digits True RMS test supported BLE 4.0 wireless transmission, more stable, less power consumption Chart and Diagram mode, to analyze your data Supports NCV Voice Broadcast simplifies testing Flashlight function Built-in offline recording function Supports Android, iOS Included Test leads K-type thermocouple 9 V Battery Bolt driver Crocodile clip Quick guide
€ 39,63
-

OWON OWON SPE6103 DC Power Supply (300 W)
The OWON SPE6103 is a 1-channel DC power supply (300 W) in a small body with features like over voltage and over current protection. It has a high resolution of 10 mV/1 mA. The 2.8' LCD displays the following information (constant voltage output, constant current output, cumulative running time, actual output power, channel output status, actual voltage output, actual current output).Features Small body for easy carry High resolution: 10 mV/1 mA List waveform editing output, editable 10 groups of timing output function Low ripple/noise Over voltage / over current protection Output voltage and current curve monitoring function Intelligent temperature control fan cooling 2.8-inch TFT LCD display USB communication interface, support SCPI Specifications Model SPE6102 SPE6103 Rated Output (0-40°C) Voltage 0-60 V 0-60 V Current 10 A 10 A Output Power 200 W 300 W USB Output 5 V/1 A (SPE Series) or suppout QC2.0, QC3.0, BC1.2, Apple, Huawei, Samsung fast charging protocols (optional) Load Regulation Voltage ?30 mV Current ?20 mA Power Regulation Voltage ?30 mV Current ?20 mA Setting Resolution Voltage 10 mV Current 1 mA Readback Resolution Voltage 10 mV Current 1 mA Value Resolution (within 12 months) (25 ±5°C) Voltage ?0.1% ±30 mV ?0.1% ±30 mV Current ?0.05% ±10 mA Readback Value Resolution (25 ±5°C) Voltage ?0.1% ±30 mV ?0.1% ±30 mV Current Ripple/Noise Voltage (Vp-p) ?50mVp-p ?50mVp-p Voltage (rms) ?5mVrms ?5mVrms Current (rms) ?30mAp-p Output temperature coefficient (0-40°C) Voltage 100ppm/°C Current 200ppm/°C Readback temperature coefficient Voltage 100ppm/°C Current 200ppm/°C Response Time (50-100% rated load) ?1.0ms Storage 4 groups of data Working Temperature 0-40°C Included 1x OWON SPE6102 1x Power Cord 1x Quick Guide 1x USB Cable 1x Fuse Downloads User Manual Programming Manual Software
€ 125,00
-

Uni-Trend UNI-T UDP3305S-E DC-voeding (328 W)
The UDP3305S-E is a high-performance programmable linear DC power supply. It has a clear LCD user interface, excellent performance indicators, a variety of analysis functions and communication interfaces. It can meet the diversified test needs of users. It aims to provide cost-effective DC programmable power supply equipment for teaching, scientific research, industry and other fields. LCD interactive interface Using a 4.3-inch high-definition display screen, it provides users with a man-machine interface with rich functions and simple operation, which can display the current set output voltage/current, actual output voltage/current and protection output voltage/current value of the power supply in real time. The functional interface is simple and comprehensive, easy to operate. One-key setting for series and parallel The series-parallel connection between CH1 and CH2 of the main channel can be realized without external connection, which simplifies the connection and makes the test easier. List/Delayer function With list and delay setting functions, it can set up to 2048 sets of data according to test requirements, and the number of cycles can reach 99999. It is used with waveform templates, which is very convenient for cycle testing and aging testing. Rich remote control interface Standard RS232 communication interface, Ethernet interface, Digital I/O and master and slave USB interfaces, can be controlled by remote connection to Ethernet, or through RS232 and USB, with the host computer software to achieve software control. Specificaties Type Linear DC power supply Channels 4 Total power 328 W Output voltage CH1/CH2: 0~30 VCH3: 0~6 VCH4: 5 V Output current CH1/CH2: 0~5 ACH3: 0~3 ACH4: 2 A Resolution 10 mV, 1 mA Setting accuracy 0.3% +20 mV<0.2% +5 mA Connectivity USB Device, RS-232, LAN, USB host, Digital I/O Inbegrepen 1x UDP3305S-E DC Power Supply 1x Power cord 1x USB cable Downloads Datasheet User manual Programming manual Software V1.0 Firmware V1.10
€ 396,54
-

Elektor Digital Elektronica Zakboek (E-BOOK)
Dit boek is een naslagwerk met praktijkgeoriënteerde formules en tabellen – en geen leerboek met uitvoerige uitleg. De schrijver heeft ook voor gecompliceerde vraagstukken handzame verklaringen, benaderingsformules en rekenvoorbeelden ontwikkeld zonder daarbij zijn toevlucht tot simplificaties te nemen. De logische indeling in 10 hoofdstukken vergemakkelijkt het opzoeken en vinden van de gewenste thema’s. In elk hoofdstuk treft u steeds de vereiste wis- en natuurkundige formules aan alsmede de belangrijkste tabellen. • Gelijkstroomkringen (inclusief de beginselen van de elektrotechniek) • Wisselstroomkringen • Dioden (berekeningen, toepassingen en gelijkrichtschakelingen) • Bipolaire transistoren • Veldeffecttransistoren (met schemavoorbeelden en berekeningen) • Speciale componenten (zoals PTC, NTC, VDR) • Operationele versterkers en hun basisschakelingen • Vermogenselektronica • Meettechniek (nauwkeurigheid, correcties, analoge en digitale meetapparaten) • Digitale technieken en binaire signaalwaarden De verzameling formules omvat alle belangrijke details voor ingenieurs en technici in de elektrotechniek en elektronica die zich met onderzoek, ontwikkeling en service bezig houden. Daarnaast is het echter ook bedoeld als naslagwerk voor studenten en docenten in het technisch (beroeps)onderwijs – en zeker ook voor de serieuze hobbyist.
€ 29,95
Leden € 23,96
-

Elektor Digital 311 circuits (E-book)
Cet ouvrage est un trésor : il réunit 311 schémas d'électronique analogique, logique ou numérique, des programmes, des liens vers des sites internet, des tableaux de caractéristiques de composants et des dessins de circuit imprimé. Il est le onzième volume de la collection « 300 circuits » (301... 311 circuits). Ses deux tables des matières alphabétique et thématique vous permettent de trouver rapidement et facilement parmi les 311 articles proposés ceux qui répondront à vos besoins. Ces articles viennent des numéros doubles récents de la revue Elektor, publiés chaque année en été, et appelés numéros Hors-Gabarit, par allusion à leur contenu exceptionnellement riche. Ils forment un véritable catalogue d'idées, de trouvailles et d'astuces. C'est une source d'inspiration inépuisable, et à partir de laquelle chacun élaborera ses propres variantes qu'il combinera ensuite à sa guise avec d'autres circuits. Tous les domaines familiers et usuels de l'électronique sont abordés : alimentations, régulateurs et chargeurs audio & vidéo communication hautes fréquences informatique jeux & modélisme maison & automobile mesure & test processeur & contrôleur robots et leurs accessoires Certaines de ces réalisations sont présentées sous une forme succincte, d'autres sont élaborées avec schéma détaillé, dessin de circuit imprimé, liste de composants complète et circuit imprimé, ces fameux circuits imprimés qui ont fait une partie de la réputation d'Elektor. Un concentré de tout le savoir-faire du laboratoire d'Elektor pour un prix modique. On y trouve beaucoup plus que ce qu'on y cherche.
€ 29,95
Leden € 23,96























